
Immuno-nutrients: Nutrients Every Child Needs for a Strong Immune System
A strong immune system is essential for keeping children healthy and resilient against infections and illnesses. Additionally, it would help the child keep track of the growth curve by reducing the risk of illness. A variety of micronutrients (vitamins C, D, E, folic acid, zinc, iron, selenium, magnesium, and copper) and macronutrients (amino acids, cholesterol, and fatty acids) are integral for immune function.(1, 2) Hence, as a parent, it is important to include immuno-nutrients as part of the daily diet to support immune system development and function.
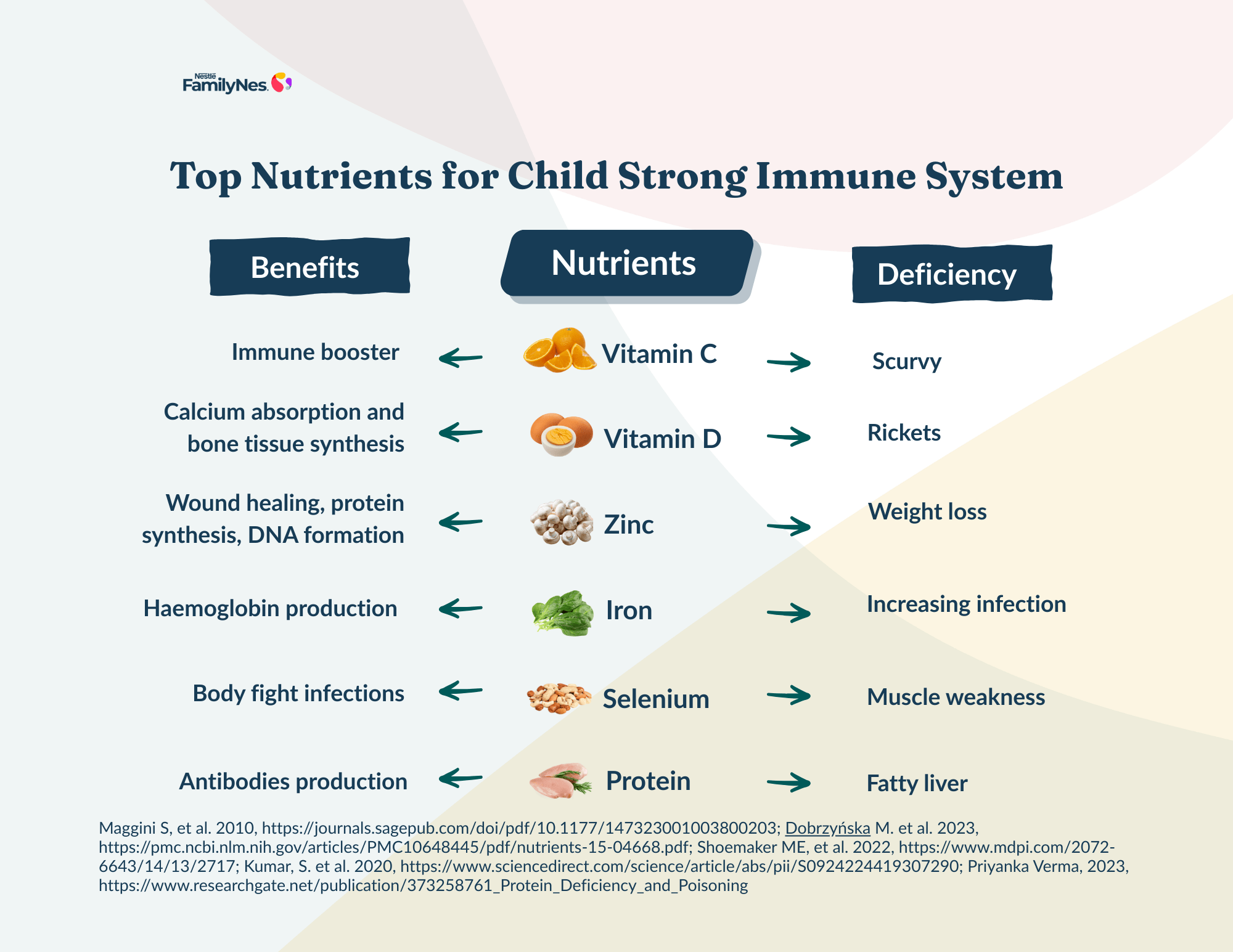
So, what is the role and importance of immune-nutrients?
Vitamin C:
Vitamin C is a vital water-soluble nutrient that supports the immune system, helps heal wounds, and protects against common flu-like illnesses, e.g., colds. Its antioxidant properties fight free radicals and enhance iron absorption, which is crucial for blood transport. Additionally, it promotes healthy skin and collagen production.
Its deficiency, often due to inadequate intake, leads to the increased probability of infections and illness. Its deficiency would also impact iron absorption, leading to anemia. Its extreme deficiency could lead to scurvy and gum bleeding.(3)
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruit, berries, mangoes, pineapples, kiwis, tomatoes, and leafy greens are a few food sources of vitamin C.
Zinc:
Zinc is essential for wound healing, protein synthesis, DNA formation, cell division, and immune function. It is important to ensure daily intake of zinc since the body cannot store it.
Zinc deficiency can impact immune functioning, slow linear growth, and cause appetite loss, hair loss, weight loss, and delayed wound healing.(3)
Include dairy products (milk, dahi), eggs, legumes (phaliyan), oats, quinoa, whole-grain breads, paneer, peas (matar), mushrooms, spinach (palak), and chicken in your children’s diet.
Selenium
Selenium is essential for maintaining immune function and helping the body fight infections.
Selenium deficiency may cause fatigue, muscle weakness, hair loss, brain fog, and a weakened immune system, increasing infection risk.(4) Thus, an adequate supply of selenium can keep the immune system functioning adequately.
Include chicken, eggs, nuts (walnut, almonds, cashew), dairy products, whole grains, sunflower seeds, vegetables, legumes, and fortified milk and food.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and bone development. Besides, it is crucial for immune regulation and helps fight off respiratory infections.
Many children have low vitamin D levels due to their changed lifestyle and reduced vitamin D intake.
Add sunlight exposure to their daily routine and fortified dairy products (fortified milk), eggs, and butter (ghee) to their diets to support intake of vitamin D.(5)
Iron
Iron is essential for haemoglobin production and regulates immune function.
Its deficiency impairs macrophages, neutrophils, and T lymphocytes production, which are the key cells of the immune system. This weakens the immune system, increasing infection susceptibility in children.
Include red meat, poultry, leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), legumes, and iron-rich fortified milk and food in their diet to support the necessary quantity intake of iron.(6)
Proteins
Protein is the fundamental component of all the cells in the body.
Adequate intake of proteins is essential in maintaining the immune system of your child. Proteins provide amino acids necessary for synthesizing immune proteins, cytokines, and antibodies, which regulate immune responses.
Deficiency may lead to affected growth, affected muscle mass, affected cell growth, increase in severity of infection, etc.(7)
Include meat, eggs, nuts, lentils, and seeds, which are good sources of protein. Making fortified milk & foods as part of daily diet would also help in meeting the daily needs of the protein.
Why Fortified milk?
Fortification plays a crucial role in supporting the intake of essential nutrients for growth and immunity. Fortified milk, with zinc, selenium, and vitamins C, D, and E, supports the optimal functioning of the immune system and helps reduce the risk of deficiencies. Fortification provides a practical solution to support the growth and development of your child by providing adequate nutrition when given along with a regular daily diet.
Remember that every child needs a well-balanced diet to ensure they get a sufficient amount of essential minerals and vitamins. It will help them stay active, grow properly, and fight off infections effectively. Encourage a variety of nutrient-rich foods to give your child the best defense against illnesses!
Talk to your paediatrician to know more about fortified milk and foods.
References
- Dunbar CL, Aukema HM, Calder PC, Gibson DL, Henrickson SE, Khan S, et al. Nutrition and immunity: perspectives on key issues and next steps. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2023 Jul;48(7):484–97.
- Munteanu C, Schwartz B. The relationship between nutrition and the immune system. Front Nutr. 2022 Dec 8;9:1082500.
- Essential Role of Vitamin C and Zinc in Child Immunity and Health - S Maggini, S Wenzlaff, D Hornig, 2010 [Internet]. [cited 2025 Mar 13]. Available from: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/147323001003800203?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed
- Dobrzyńska M, Kaczmarek K, Przysławski J, Drzymała-Czyż S. Selenium in Infants and Preschool Children Nutrition: A Literature Review. Nutrients. 2023 Nov 3;15(21):4668.
- Shoemaker ME, Salmon OF, Smith CM, Duarte-Gardea MO, Cramer JT. Influences of vitamin D and iron status on skeletal muscle health: A narrative review. Nutrients. 2022 Jun 29;14(13):2717.
- Shubham K, Anukiruthika T, Dutta S, Kashyap AV, Moses JA, Anandharamakrishnan C. Iron deficiency anemia: A comprehensive review on iron absorption, bioavailability and emerging food fortification approaches. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2020 May 1;99:58-75. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0924224419307290
- Priyanka Verma. Protein Deficiency and Poisoning. Research & Reviews: A Journal of Medicine. 2023; 13(1): 9–14p. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373258761_Protein_Deficiency_and_Poisoning

