
Building Healthy Smiles: Supporting Teeth Development in Toddlers
As a mother, ensuring your child has strong, healthy teeth is just as important as their overall growth and development. Oral health during toddlerhood plays a crucial role in chewing, speaking, and setting the foundation for permanent teeth. Nutrition and hygiene are key to developing strong and healthy teeth.
The First Teeth: A Milestone in Development
Teething usually begins around 6-7 months of age, and by the time a child turns 3 years old, they typically have all 20 primary (milk) teeth. These baby teeth are temporary, but they are essential for proper digestion, speech, and jaw development.(1) Keeping these teeth cavity-free and healthy with nutrition & proper oral hygiene is important since the permanent teeth continues to develop underneath them.
Signs of Healthy Teeth in Toddlers
A toddler with good oral health will have:
- Cavity-free teeth with no discoloration or decay
- Pink, non-swollen, or non-bleeding gum
- The ability to chew food is pain-free and comfortable
- No pain or sensitivity while brushing
Regular brushing, a healthy diet, and routine dental checkups help maintain these signs of good dental health.(2)
The Growing Concern: Tooth Decay in Toddlers
Did you know that 60-80% of Indian children suffer from gum diseases and tooth decay?(3)
One of the leading causes of tooth decay in toddlers is excessive sugar intake, keeping sugar-sweetened food or beverages in the mouth for long, non-rinsing of mouth post food/ milk consumption, which fuels bacterial growth in the mouth and increases the risk of cavities. If left unchecked, this can further intensify cavities, pain, and even infections. signs of tooth decay include:
- Brown or black spots on the teeth
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, or sour foods
- Pain while eating or drinking
To prevent cavities, limit sugary snacks and drinks, and ensure your toddler has good oral hygiene and the diet is rich in essential nutrients that support overall tooth development and health.
Key Nutrients for Strong and Healthy Teeth
Optimal nutrition provides the vitamins and minerals necessary for the development and strength of teeth.(4), (5)
- Calcium: Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt, as well as leafy green vegetables, are enriched with calcium, which is necessary for healthy tooth enamel.
- Vitamin D: Required to help the body absorb calcium, is essential for bone and tooth strength.
- Phosphorus: Foods rich in phosphorus, like eggs and meat, are good for your toddler's teeth.
- Vitamin A: Carrots and sweet potatoes enriched with vitamin A are important for maintaining healthy gums and soft tissue lining the mouth.
- Vitamin C: Good for gum health and help prevent gum disease. Foods rich in vitamin C are oranges and strawberries.
- Fluoride: Drinking water with fluoride could also protect the teeth against decay. However, excess fluoride negatively affects enamel formation and contributes to an increased risk of cavities.
How Fortified Milk with Key Nutrients Necessary for Supporting Toddler Dental Health?
Milk is often considered a staple in a toddler’s diet, and fortified milk takes it a step further by providing additional essential nutrients for strong teeth and bones.
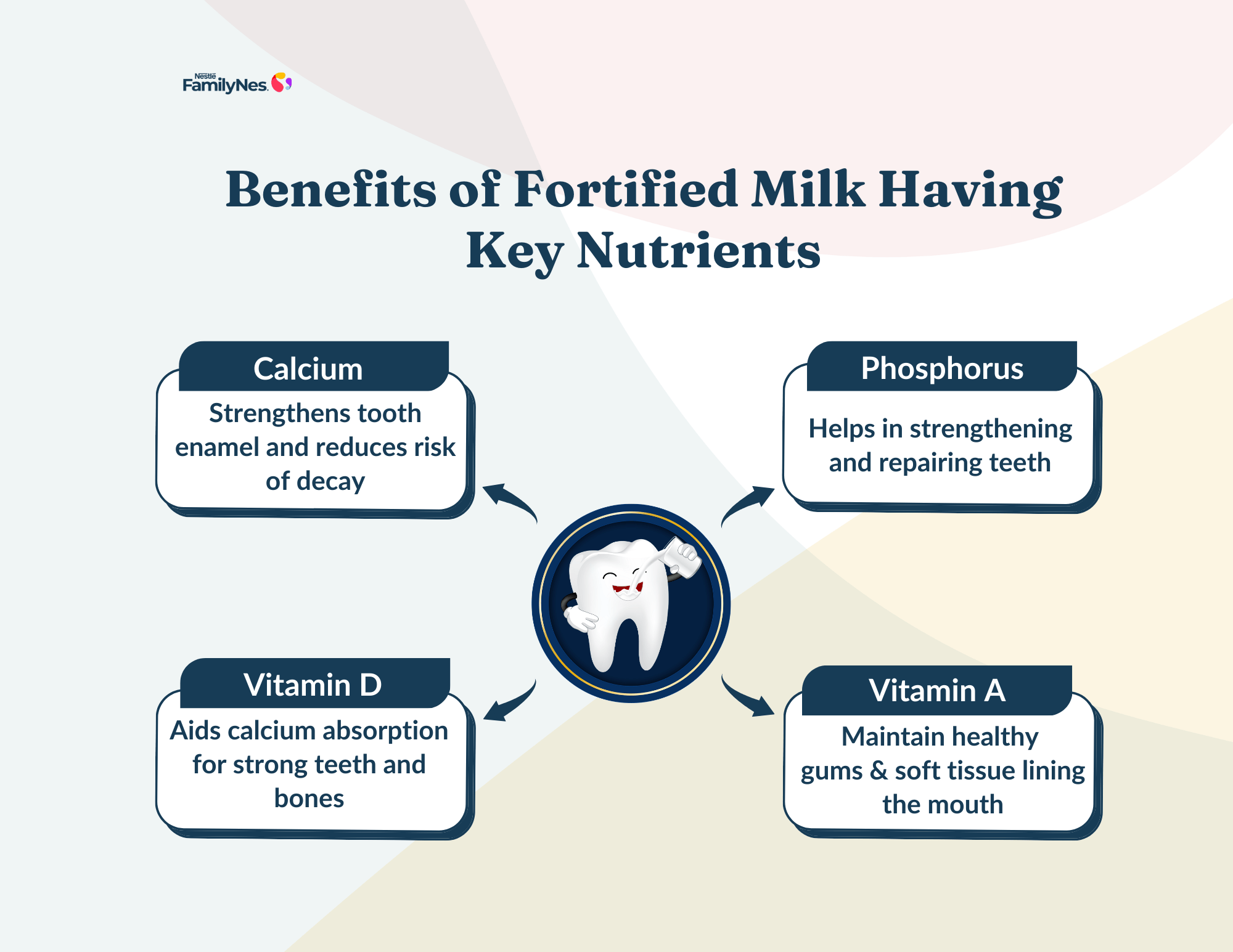
Benefits of Fortified Milk Having Key Nutrients Contributing to Oral Health:
- Rich in Calcium & Phosphorus – Strengthens tooth enamel and reduces the risk of decay.
- Contains Vitamin D – Aids calcium absorption for strong teeth and bones.
- Contains Vitamin A- Maintain healthy gums and soft tissue lining the mouth
Additional tip: Limit Sugary & Sticky Foods
Avoid sticky candies, excessive sugar-sweetened and carbonated drinks, juices, and starchy snacks like chips, which stick to teeth and increase the risk of cavities.
The Bottom Line
Building strong, healthy teeth starts early! A nutritious diet, rich in fortified milk which has essential nutrients, along with proper oral care, helps positively influence your child’s teeth and sets the stage for lifelong oral health.
References
- Moon RY, Tanabe KO, Yang DC, Young HA, Hauck FR. Pacifier use and SIDS: evidence for a consistently reduced risk. Matern Child Health J. 2012 Apr;16(3):609–14.
- Chawłowska E, Karasiewicz M, Lipiak A, Cofta M, Fechner B, Lewicka-Rabska A, et al. Exploring the Relationships between Children’s Oral Health and Parents’ Oral Health Knowledge, Literacy, Behaviours and Adherence to Recommendations: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 8;19(18):11288.
- Indian Pediatrics - Editorial [Internet]. [cited 2025 Mar 24]. Available from: https://www.indianpediatrics.net/nov2002/nov-1001-1005.htm
- Naidoo S, Myburgh N. Nutrition, oral health and the young child. Matern Child Nutr. 2007 Sep 4;3(4):312–21.
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD). Guideline on Infant Oral Health Care. Accessed as: https://www.aapd.org/assets/1/7/g_infantoralhealthcare.pdf

